TIG Welding Mastery: A Guide to Your First TIG Welder
Supercharge your TIG welding skills with this FREE guide.
This article is a FREE TIG welding guide.
You want to enhance your TIG welding skills, techniques, and knowledge to launch your career as a professional TIG welder? If you actually make it through this article and understand the content, congratulations! You’re officially proficient. And proficient welders get first dibs on the best welding jobs.
I want you to start that welding career if you’re up for a solid income, working with your hands, and, let’s be real, having way more fun than a career with a desk job.
Quick Facts
TIG welding is known for precision and versatility and can make clean welds on all metals, making it perfect for the aerospace and automotive industries.
TIG welding requires a skilled operator as it’s more complex, slower and requires more control over heat, gas flow and movement which can even challenge experienced welders.
The key to TIG welding is understanding the equipment setup, selecting the right power source and features, maintaining the welder and following safety practices to get the best performance and quality.
TIG Welding Mastery
TIG welding is favored for its precision and can make high quality welds.
This welding process excels in making clean strong joints due to its precise control over heat input and welding speed. It’s the choice for applications that requires attention to detail, like aerospace and automotive industries. But what makes TIG welding different from other welding processes?
One of the benefits of TIG welding is its versatility. It can weld on all metals, aluminum, copper and stainless steel, makes it suitable for many applications.
But TIG welding is not without challenges. It’s said to be more difficult to master than other welding processes, requires more coordination and practice. The process is slower which can affect productivity. And a skilled operator is required to get good results.
Understanding TIG Welding
TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), is a precise and versatile welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce high-quality welds.
This method is renowned for its ability to create clean, strong joints on a variety of metals, making it a favorite in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing.
The combination of non consumable electrode and precise control of the process gives high quality results in many applications, including gas tungsten arc welding.
If you get really good at TIG welding you can apply for the high paying jobs like aerospace welding and pipe welding.
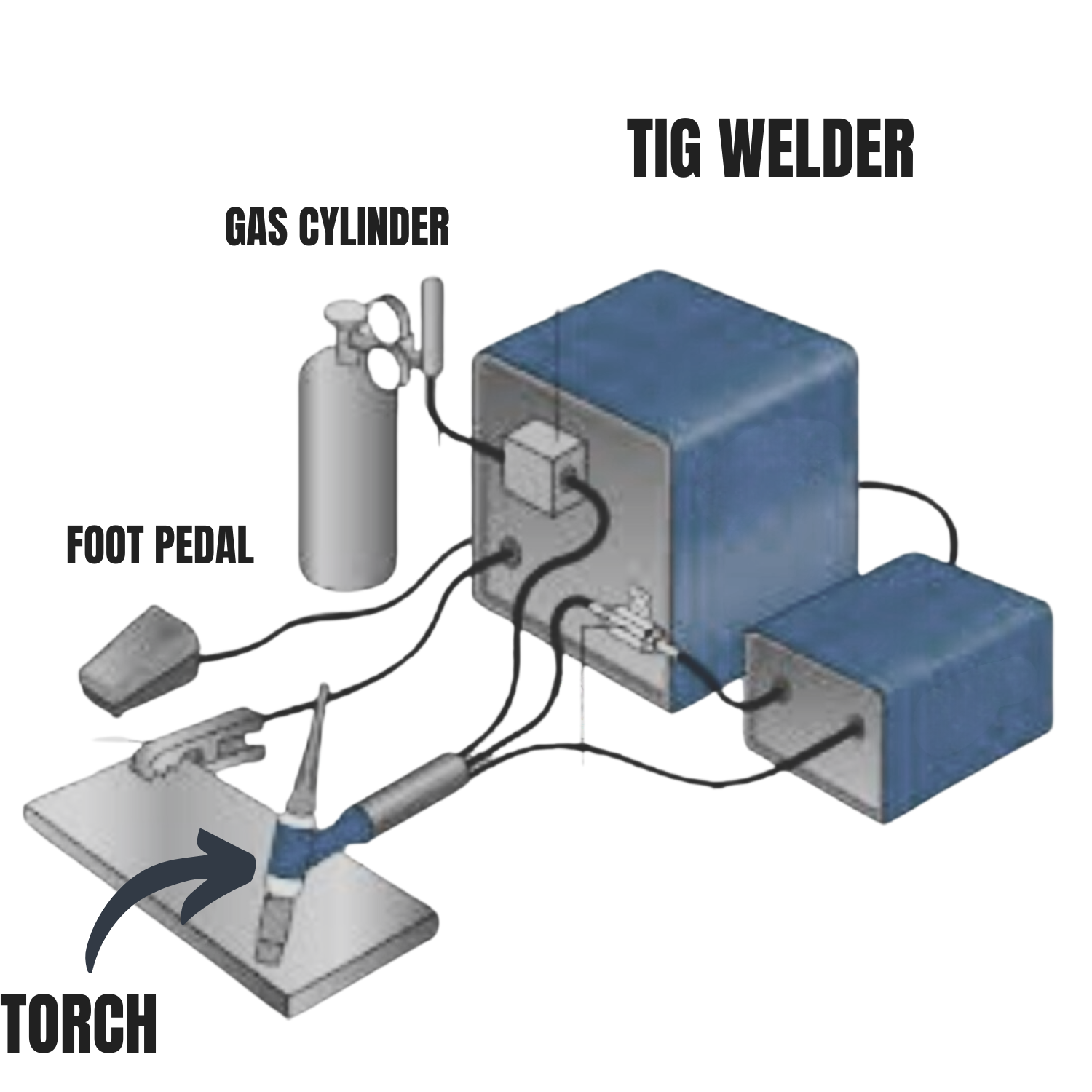
How a TIG welder works for beginners :
.
The diagram above shows a TIG welding setup. It depicts the proper set up for your TIG welder. TIG welder, gas cylinder, foot pedal, and torch, illustrating the components needed for TIG welding.
.
How a TIG torch works for beginners:
STEP 1 The process begins with the tungsten electrode, which generates a high-temperature arc when an electrical current passes through it.
This arc melts the base material, forming a weld pool—the molten metal that will solidify into the weld. The welder must carefully control this weld pool to ensure a strong, defect-free joint.
STEP 2 A critical component of TIG welding is the shielding gas, typically argon or helium.
This gas flows around the weld area, protecting it from atmospheric contamination such as oxygen and nitrogen, which can cause oxidation and weaken the weld. The shielding gas also helps maintain a stable welding arc, which is essential for producing consistent, high-quality welds.
STEP 3 In many cases, a filler rod, or filler wire, is used to add material to the weld pool, reinforcing the joint and ensuring its strength.
The welder must skillfully feed the filler rod into the weld pool while maintaining control over the arc and the shielding gas flow.
That is basically TIG welding. By understanding these fundamental aspects of TIG welding, you can begin to appreciate the complexity and precision involved in this versatile welding technique. Whether you’re working with aluminum, stainless steel, or carbon steels, mastering TIG welding opens up a world of possibilities for creating strong, clean, and aesthetically pleasing welds.
TIG Welding Basics
These easy techniques will improve your entire life.
Travel Speed
Travel speed is the rate at which you move your torch across the base metal while welding. TIG welding requires a high level of skill and technique. The welder must manage the heat input, control the welding arc, and maintain the correct distance between the tungsten electrode and the workpiece while maintaining the travel speed. This precision is what allows TIG welding to produce such high-quality results, but it also means that mastering this process takes practice and patience.
Heat Control
The key to its success is the precise control of heat input and welding speed to get clean and strong TIG weld joints. Tungsten inert gas welding is a must skill for welders who wants to be excellent.
Gas Coverage
The inert gas shielding in TIG welding prevents oxidation and contamination which is very important to maintain the integrity and appearance of the welds. When welding, be careful how you angle the torch because when doing so you are moving the gas around.
Tip: try your best to keep your torch angle perpendicular to the weld joint.
Practice. Master the control of heat input, gas flow and travel speed to get the desired weld quality. With the right technique and practice TIG welding can be a very rewarding skill.
This process can weld on many metals making it very versatile for many applications. But requires a skilled operator to execute as it’s more difficult to master than others.
Compared to MIG welding, TIG welding requires more skill and time but has more control of the process and gives higher quality welds. TIG welding is used in many industries such as automotive, aerospace and medical equipment manufacturing. Despite the slower pace and higher skill requirement, the quality and precision of TIG welding makes it a valuable technique in the welding world.
Image: TIG welding supplies, including TIG torch, TIG cup, gas lens, collet, and other essential welding consumables for precise TIG welding.
TIG Welder Components
Knowing the components of a TIG welder gives high quality welds.
The tungsten electrode is a crucial part of the TIG welding process, it’s an electrode that doesn’t burn up during welding. Depending on the task the tungsten electrode can be sharpened to a point or ball shape. This flexibility allows welders to adapt to different welding needs and have precise control of the weld pool.
Gas cylinder and regulator. Besides the tungsten electrode, a gas bottle and regulator is required for gas delivery. Argon gas is commonly used to protect the weld from airborne contaminants to get a clean and strong bond. When welding nickel alloys, it is essential to use specific gas mixtures to enhance the welding process and protect the weld from oxidation and contamination.
The torch nozzle with gas lens ensures gas flow and protection for the arc and the weld pool. The work lead attaches to the workpiece or metal surface to complete the electrical circuit for welding.
Accessories like welding covers, water coolers and water-cooled TIG torches can further enhance the welding machine.
Choosing the Right TIG Welder
Choosing the right TIG welder can be overwhelming with many options available in the market. Prices of TIG welders vary greatly, from portable units for $500 to professional-grade machines for over $5,000. Your needs and budget should be your guide in choosing the welder. We are experts and can help you pick the right TIG welder for you.
The power source is a key factor to consider when choosing a TIG welder. The power source can be alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC) depending on the materials being welded. AC is used for aluminum welding while DC is used for steel and other metals. Knowing the power source options and their applications will help you make an informed decision.
Power Source Options
The power source of a TIG welder can be alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC) depending on the materials being welded.
AC is used for aluminum welding as it breaks up the oxide layer on the surface of the metal. DC is used for steel and other metals for a smooth and stable arc. Knowing the differences between these power sources and their applications is key to choosing the right TIG welder.
Key Features to Consider
Several features can improve your welding experience and weld quality when choosing a TIG welder.
A foot pedal gives you precise heat control and frees up both hands to handle the torch and filler rod. This is especially useful for consistent weld quality and overheat the material. This is the skill you want to practice to become an aerospace welder. These welders are the free-hand TIG welding champions. Heat control. Geat heat control is foundational in mastering TIG welding.
Pulsed welding technology is another great feature, it gives you more control over heat input and prevents burn-through on thin metals. This is especially useful when working with delicate or thin materials, it helps to maintain a stable weld pool without excessive heat. A high frequency setting also improves arc stability which is crucial for TIG welding.
Water-cooled torches are good for high power applications as it keeps the temperature lower and allows for more precise and detailed work. The design of the TIG torch itself can vary, with options for built-in controls or separate foot pedal. These features can greatly impact the usability and performance of the TIG welder so it’s important to consider when choosing a machine.
Setting Up Your TIG Welder
Setting up your TIG welder correctly is key to getting good welds and safe operation.
One of the first step in the setup is to connect the ground clamp to the workpiece, this completes the electrical circuit for welding. Make sure it’s solidly connected to prevent electrical issues and for a stable arc.
Adjust the gas flow to shield the weld pool.
30 cubic feet per hour (cfh) is a good gas flow for most TIG welding applications. For aluminum welding use alternating current (AC) mode, for other applications use direct current electrode negative (DCEN) polarity.
Use a foot pedal when possible.
The foot pedal controls the arc and fine tunes the heat input so it’s important to set up. The initial setting on the machine is just a guide and you may need to adjust based on the application.
TIG Welding Techniques: Managing the Weld Puddle
Simple TIG welding techniques are key to getting good welds. Understanding the formation and behavior of the weld puddle is critical, as it determines the width and penetration of the weld. One of the basic techniques is to maintain the correct torch angle.
Follow these 3 simple steps:
STEP 1 The torch should be held at about 20 degrees from vertical to help form the weld pool better.
This angle directs the heat and shielding gas to the weld pool and helps to keep it stable and clean.
STEP 2 Travel speed during TIG welding affects the heat-affected zone and overall weld quality.
1mm per second is a good travel speed but it can vary depending on the material and thickness. Effective heat control is crucial in TIG welding and is controlled by adjusting the arc from the torch, this allows you to control the size and shape of the weld pool and get consistent good welds.
STEP 3 A consistent distance between the tungsten and the workpiece prevents contamination and gets good welds.
Ideally, it should be within 1mm. Using the correct filler rod angle, about 15 degrees from horizontal, gives you better control when adding filler metal to the weld pool. These techniques when practiced and mastered will greatly improve your TIG welding.
Working with Different Metals
TIG welding is known for its versatility, welders can work with many metals including exotic metals like titanium and magnesium.
This versatility makes TIG welding very valuable in many industries like aerospace and automotive manufacturing. Depending on the metal, the power source of the welder can vary; for example AC is often used for aluminum, DC for steel.
Aluminum has its own challenges because of its lower melting point than stainless steel.
Special techniques and a steady hand is required to weld these metals together. For welding dissimilar metals like stainless steel and aluminum, using a hybrid filler rod like ER309L can help accommodate their differences and get a strong bond. Experimenting with different filler rod materials can also help with compatibility with the base metal.
Clean the surfaces of the metals before welding.
The surfaces should be clean and free of contaminants to get a strong bond and prevent weld porosity.
Oxidation and discoloration can occur if the shielding gas is not adequate or contaminated, it will affect the appearance and integrity of the weld. Focus on the base metal temperature before welding will improve the overall weld quality.
TIG Welding Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Even experienced welders can make common mistakes that can affect the quality of their welds. One common mistake is improper TIG welding speed. When the speed is too fast the weld beads will penetrate through the back of the steel and will result to weak joints. Make sure to get the correct travel speed to maintain the integrity of the weld and prevent this.
Another common mistake is inadequate shielding gas coverage which can cause oxidation and contamination of the welds. Since TIG welding does not use flux the welds do not require extensive post weld cleaning so you can spot any issues early on.
Pay attention to these details and make the necessary adjustments to improve weld quality and prevent common welding defects.
TIG Welder Maintenance and Care
Take care of your equipment.
Regular maintenance will improve performance and extend the life of your TIG welder. Scheduled professional servicing will maintain the functionality and safety of the welder. Keep the welder clean from dirt and grime as buildup can affect the cooling of internal components.
Inspect and clean the torch regularly to get good gas flow and prevent welding defects. Keeping the tungsten electrode is also important; improper grinding or using the wrong current can cause faster wear. Tungsten inclusions can occur when particles from the electrode embed in the weld, usually from touching the electrode to the weld pool.
Grounding the electrical network used for TIG welding is important to avoid electrical hazards. Follow these tips to keep your TIG welder in good condition and get consistent good welds.
TIG Welding Safety Tips
This is the most important tip.
Safety first when it comes to TIG welding. A well prepared workspace should be clean, well ventilated and free from flammable materials to minimize risk. The gas cylinder used for TIG welding should be secured upright during operation. Unplug the machine before doing any maintenance work to ensure safety.
Welders should wear a welding helmet with filter glasses to protect against the UV and IR radiation produced during welding. Cover the body with protective clothing to prevent skin damage from direct UV radiation.
Ventilation system should be installed to remove harmful fumes and dust during TIG welding. Argon gas used in TIG welding can displace oxygen in enclosed spaces and can cause hypoxia to the welder. Follow these safety tips to create a safer welding environment.
Advanced TIG Welding Tips
Advanced techniques can improve weld quality for those who wants to fine tune their TIG welding skills. One of these techniques is using the pulse setting on your TIG welder which controls heat input and reduces distortion. This is useful when welding thin materials as it prevents burn through and maintains the integrity of the weld.
Precision welding and heat control can improve weld quality. For example maintaining a consistent torch angle and travel speed and using the correct filler rod angle can get you clean and strong welds. Experimenting with different filler rod materials and adjusting base metal temperature before welding can improve compatibility and weld quality.
Mastery of these advanced techniques will get you awesome results, level up your welding skills, and have a great life.
Conclusion
In summary, TIG welding is a precise and versatile welding technique that offers many advantages including high-quality and good looking welds. Perfect for welding rockets like the aerospace welders at SpaceX. Knowing the basics, choosing the right equipment and mastering the fundamentals are the keys to become proficient in TIG welding. Regular maintenance and following safety protocols will extend the life and performance of your welding setup.
As you get more practice and fine tune your skills remember the advanced tips and techniques to improve your weld quality. With discipline and attention to detail you can get awesome results and take on any welding project.
FAQs
What are the advantages of TIG welding?
TIG welding is precise and high quality with minimal splatter suitable for aluminum, copper and stainless steel. That’s why it’s versatile in many applications.
What to consider when choosing a TIG welder?
When choosing a TIG welder consider your specific needs, budget and the power source required for the materials you will be welding. Also consider foot pedals, pulsed welding technology and water cooled torches for better performance.
How to set up my TIG welder?
To set up your TIG welder attach the ground clamp to the workpiece, adjust the gas flow to 30 cfh, set the polarity to AC for aluminum and DCEN for most other applications and use the foot pedal for heat control.
What are the common TIG welding mistakes and how to avoid them?
To avoid common TIG welding mistakes like wrong welding speed and insufficient shielding gas coverage make sure you maintain the right travel speed and provide enough gas flow. This will prevent oxidation and contamination in your welds.
How to maintain my TIG welder?
To maintain your TIG welder properly clean the machine, inspect and clean the torch and maintain the tungsten electrode and make sure it’s grounded. Schedule professional servicing to extend its life and safety.